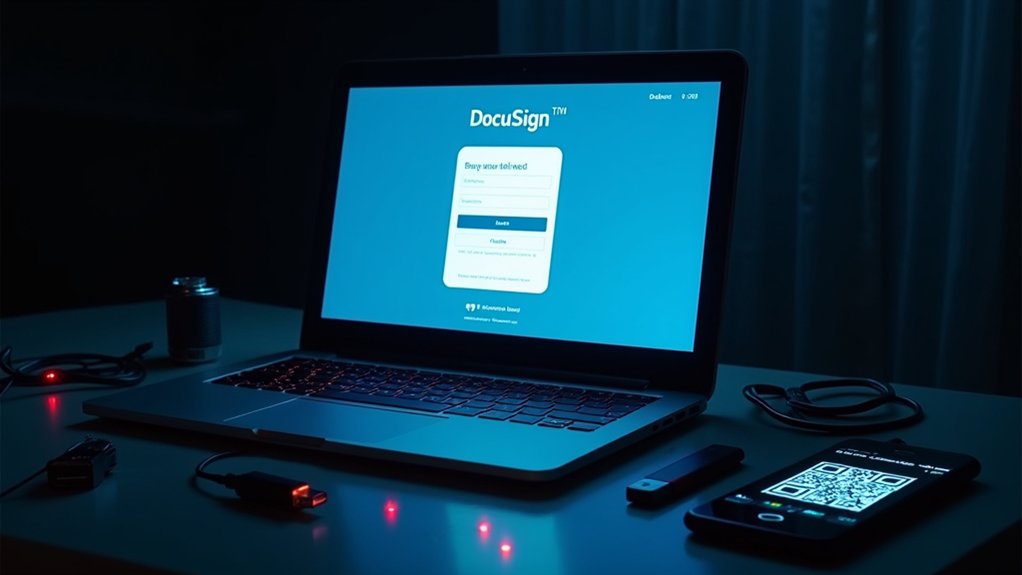
How quickly can cybercriminals adapt trusted platforms to deceive unsuspecting users? The answer lies in the dramatic surge of phishing campaigns exploiting DocuSign’s reputation, with fraudulent activity increasing 98% since November 8, 2024, particularly targeting state agencies and their business partners.
Threat actors have evolved beyond simple email spoofing, now registering authentic DocuSign accounts to transmit seemingly legitimate envelopes containing fraudulent invoices. These sophisticated campaigns utilize DocuSign’s massive userbase of over one billion users globally, with attackers especially focusing on the 95% of Fortune 500 companies that utilize the platform. By May 2025, phishing represented 19% of initial access vectors, escalating to 60% of total breaches according to the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report. Implementing strong authentication methods can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to legitimate accounts.
Cybercriminals now exploit legitimate DocuSign accounts to bypass security measures, targeting Fortune 500 companies through trusted platform abuse.
The methodology demonstrates alarming sophistication, as cybercriminals exploit legitimate DocuSign solutions and APIs to craft convincing fraudulent documents. Recipients receive urgent notifications mimicking envelope communications from regulatory agencies, complete with conspicuous “review document” prompts that redirect users to credential-harvesting sites designed to replicate Microsoft or DocuSign login pages. Some campaigns incorporate QR codes within attachments, particularly targeting mobile devices that often lack enterprise-grade security controls.
Government entities bear the brunt of impersonation attempts, with attackers spoofing communications from the Department of Health and Human Services, Maryland Department of Transportation, and City of Milwaukee. These fraudulent messages target contractors, suppliers, and businesses that regularly interact with state and municipal agencies, exploiting established trust relationships to maximize success rates. The human element accounts for 68% of breaches, with 80-95% of these incidents initiated through phishing attacks that exploit these trusted relationships.
Detection poses significant challenges as tactics evolve rapidly to outpace traditional security methods. The exploitation of legitimate DocuSign accounts for malicious purposes complicates identification efforts, while the platform’s trusted brand presence reduces recipient suspicion. Hundreds of phishing instances are now detected daily, with common themes including Norton, PayPal, and Remittance Advice impersonations alongside DocuSign exploitation. DocuSign has implemented technical systems specifically designed to counteract these phishing attempts and prevent service misuse.
The combination of legitimate account abuse with traditional spoofing techniques creates a formidable threat environment. As compromised DocuSign accounts send requests to other DocuSign users, the trusted relationship between businesses and regulatory authorities becomes a vulnerability that cybercriminals continue to exploit with increasing frequency and sophistication.